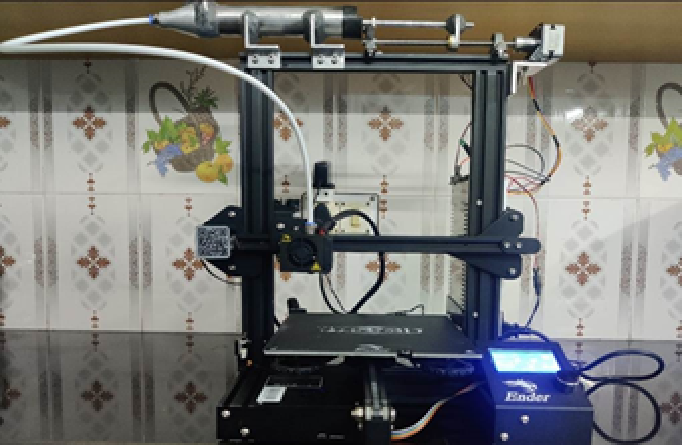
Innovator Name: Dr. Suraj Marathe
Contact No: +918554919805
Contact Email: suraj_marathe@rediffmail.com
Abstract:
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is the construction of a 3-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model. The term “3-D printing” can refer to a lot of methods wherein material is deposited, joined, or solidified under computer control to create a 3D object, with material being delivered together (including liquid molecules or powder grains being fused together), generally layer by layer.
One of the important benefits of 3-D printing is the ability to supply overly complicated shapes or geometries that might be in any other case not possible to assemble by hand, which include hollow elements or parts with internal truss structures to lessen weight.
Since it was introduced, it has the potential to massively disrupt both the manufacturing logistics and inventory management industries, if it can be successfully incorporated into mass production processes. The technology has been used to reduce the lead time in the development of prototypes of parts and devices, and the tooling needed to make them. This is hugely beneficial to small-scale manufacturers because it reduces their costs and the time to market (the amount of time from a product being conceived until its being available for sale), because 3-D printing can create intricate and complex shapes using less material than subtractive manufacturing processes, such as milling, it is used in hydroforming, stamping, injection moulding, and other processes.